Abstract
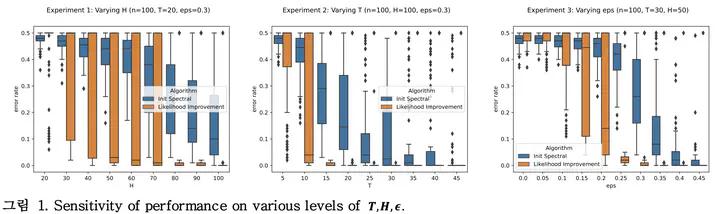
Reinforcement learning (RL) has been shown to be effective by utilizing the low-dimensional representations of an environment. This approach is formalized by imposing structural assumptions on the Markov Decision Process (MDP). Herein, we focus on the Block MDP (BMDP), where contexts are clustered and where observable transitions are governed by latent state transition. A recent study proved a lower bound for the clustering error of BMDP and proposed a two-step algorithm with a performance guarantee that nearly matches the lower bound. In the current paper, we empirically validate their results of that recent study by implementing and simulating the algorithm in a synthetic, non-regular BMDP environment. In what is perhaps the most surprising finding, random trajectory corruption up to a certain level actually aids clustering performance, which resembles the implicit regularization phenomenon that has been researched in label noise SGD in the deep learning theory community.